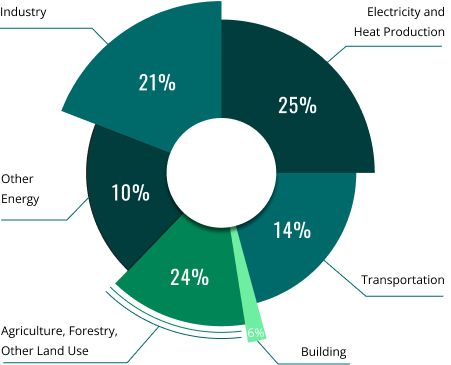
The Agriculture, Forest, & Other Land Use sector contributes approximately 24% of the total global emissions, not only through the energy used for cultivation but also in the management of lands.
However, plants play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing a portion of that carbon in biomass, dead organic matter and soil. This carbon storage process is referred to as biological carbon sequestration.
Therefore, the combination of natural carbon sequestration and effective land management can be regarded as a form of "negative emission" technology.
Soils have the capacity to absorb over a billion tons of carbon annually.
Implementing less intensive tilling practices, mulching parts of the crop, and incorporating intermediate crops for green manure create significant opportunities to sequester carbon absorbed from the atmosphere for an extended period.